- October 25, 2024
Introduction
In the technological world, computer vision & machine vision help automate tasks and improve efficiency in many industries. Although people often mix them up, they are different technologies with their own uses. Knowing the difference helps businesses use visual data to make their operations better.
Computer vision, a part of AI, helps machines understand and interpret images and videos, much like human vision. It gathers useful information from what it sees. On the other hand, machine vision is made for industrial tasks, like automating inspections and quality control in factories.
Basics of Computer Vision and Machine Vision
What is Computer Vision:
- Aims to enable machines to interpret visual data.
- Utilizes advanced algorithms, machine learning, and deep learning techniques.
- Capable of analyzing both real-time images and stored visuals.
- Applications of computer vision includes facial recognition, object detection, and augmented reality.
What is Machine Vision:
- Integrates cameras and software into machines for specific tasks.
- Focuses on making rapid decisions based on captured images.
- Typically used in controlled environments like factories.
- Applications include quality inspection, barcode reading, and part measurement.
Key Differences of Computer Vision and Machine Vision:
Purpose:
- Computer vision is broader, aiming to understand images comprehensively.
- Machine vision is task-specific, designed for operational efficiency.
Data Processing:
- Computer vision processes complex data using advanced algorithms.
- Machine vision employs simpler algorithms for quick decision-making.
Hardware Requirements:
- Computer vision can operate without dedicated hardware; it can analyze saved images.
- Machine vision requires specific hardware components like cameras and processors.
Environment:
- Computer Vision: Can function in various environments, including outdoor settings or dynamic scenarios where conditions change frequently.
- Machine Vision: Typically operates in controlled environments like factories where lighting and conditions are optimized for consistent performance.
Industry use of Computer Vision and Machine Vision :
Industries using computer vision:
- Healthcare: Medical imaging technologies use computer vision for diagnosing diseases through X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on computer vision to navigate
- Retail: Stores use computer vision for inventory management, customer behavior analysis, and checkout automation through facial recognition.
Industries using machine vision:
- Manufacturing: Used extensively in quality control processes to identify defects in products during assembly.
- Food Industry: Inspects food items for quality assurance by checking for contaminants or proper packaging.
- Logistics: Utilizes barcode reading systems for inventory management and tracking shipments.
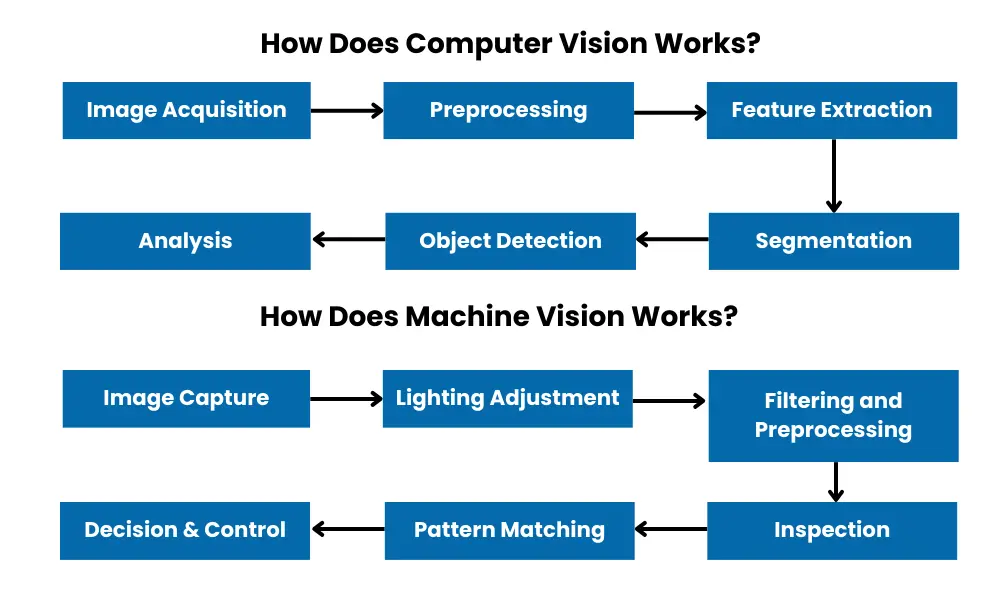
Technology Basics for Computer and Machine Vision : How they Work?
Computer Vision:
- 1. Image Acquisition: Captures images using cameras or retrieves them from databases.
- 2. Preprocessing: Enhances image quality by adjusting brightness or removing noise.
- 3. Feature Extraction: Identifies key attributes within the image using algorithms.
- 4. Segmentation: Divide image into meaningful regions for focused analysis.
- 5. Object Detection/Recognition: Identify and classify objects or patterns.
- 6. Analysis and Decision Making: Interpret results and output actions or insights.
Machine Vision:
- 1. Image Capture: Utilizes high-resolution cameras to take images of product.
- 2. Lighting Adjustment: Control lighting for optimal visibility and contrast
- 3. Filtering and Preprocessing: Enhance image clarity (e.g., edge detection, thresholding).
- 4. Inspection/Measurement: Measure dimensions, position, or defects in objects.
- 5. Pattern Matching: Compare captured features with predefined patterns or templates.
- 6. Decision & Control: Generate outputs for process control or quality assessment.
Technologies Used in Computer Vision
Deep Learning Frameworks:
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- Keras
Image Processing Libraries:
- OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library)
- scikit-image
Hardware:
- High-resolution cameras (2D and 3D)
- GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) for accelerated processing
- Specialized sensors (LiDAR, infrared cameras)
Technologies Used in Machine Vision
Cameras and Sensors:
- Industrial cameras for high-speed image capture
- Proximity sensors for detecting object presence
Lighting Systems:
- LED, fluorescent, and infrared lighting to enhance image quality.
Machine Vision Software:
- Custom software solutions that analyze visual data using predefined rules and algorithms.
The growing Market of AI and Computer Vision
The integration of AI with computer vision is revolutionizing various sectors. The market for computer vision technology is projected to reach USD 48.6 billion by 2022, driven by advancements in deep learning algorithms and increased demand for automation across industries.
Key Trends
- Smart Manufacturing: Companies adopt computer vision systems to enhance production efficiency and reduce errors.
- Healthcare Innovations: AI-powered imaging tools improve diagnostics through better image analysis.
- Retail Applications: Retailers use computer vision for inventory management and customer behavior analysis.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between computer vision and machine vision is key to picking the right technology for specific tasks. Machine vision is ideal for factory automation, focusing on speed and efficiency, while computer vision can handle more complex visual data. As AI advances, both will play a big role in improving industries, boosting productivity and quality in ways we could not imagine before.